HOME|Ideas and resoueces for planetary science experiments|Shaky Earth Project~The science of phenomena due to earthquakes(2004)
宇宙の実験教室
Ideas and resoueces for planetary science experiments
カテゴリ
Category
- 実験教室Idea and Resources for Space science experiments
- 対象項目別Category: Contents
- 学年単元別Category: Study Age
-
- 実践授業Activity Reports
タグ
Tag
 地球ブルルン大研究~地震が起こす現象の科学~(2004)
地球ブルルン大研究~地震が起こす現象の科学~(2004)
はじめに
はじめに
フレンドシップ事業では、理科教育専攻の3年生が授業の一環として理科実験のプログラムを作成し、夏休みに中学生を宮教大に迎えて理科の実験指導を行うものです。
目的
本コースでは、地震が発生するメカニズムと、地震によっておきる現象、特に、津波と液状化現象の発生メカニズムについて、実験を通して理解することを目的とした。
2003年に発生した宮城県沖付近を震源とする一連の大地震の経験や、宮城県沖地震が高確率で発生するという予測など、対象の宮城県内の中学生にとって、地震は身近な災害として捉えられると考えられる。そこで、地震について理解を深め、地震のメカニズムや地震によって発生する現象のメカニズムを、実験を通して教えていきたいと、学生の思いが集約された。
実験プログラム内容
午前中に地震の発生メカニズムについて、午後に地震によっておこる現象について、実験や観察を中心にそれぞれ学習した。
授業の流れ
| 目 的 | 実 施 項 目 |
地震発生のメカニズムを理解しよう
震源分布とプレート位置は相関がある 断層活動によって地震が発生する |
|
地震によって起きる現象を理解しよう
地形の幅が狭くなると波高が高くなる 液状化は、水量が多い場合におきる |
|
地震の発生メカニズム
地震発生のメカニズム
午前中は、主に、地震の発生メカニズムについて、身近な地震体験から導入にはいり、震源・震央など地震用語の定義、プレート運動との関係、構造運動と地震について学習した。
- 導入:地震の実体験から動機付けを行い、地震用語の定義を確認し、世界の震央分布の観察から震源分布が偏りを注目する。
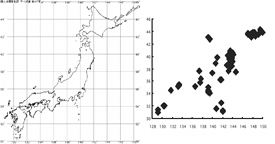
- 日本周辺域の震源分布とプレート運動:深さ別の震源分布の観察(図1)から、日本周辺域の震源分布がプレートの位置と相関している様子を観察させる。さらに、プレート運動再現装置(図2)でプレートを引きずり跳ね返す様子をモデル化したものを観察させる。
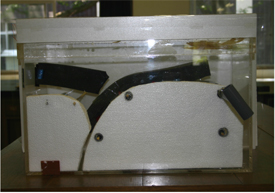
- 断層運動による地震:プレート境界型地震以外に内陸性の活断層等、浅い断層型地震があることを震源分布から読みとらせる。牛乳パックで固めた直方体の寒天を大地と見たて、上面と横1面がないアクリル板で作ったケースに入れて横から寒天を押し亀裂が入ることを観察する断層形成のモデル実験(図3 )を実施し、東北工大青葉山グラウンドの断層の写真を観察する。
 |
 |
| 図1 深度別震源分布シート(左)。過去10年間の日本周辺で発生した地震の震源(理科年表)を地表から100kmの深さまで10km単位にOHPシートにプロットしたもの。(右)震源分布シートを深さ順に上下に重ね新家分布の特徴を観察している生徒。 | |
 |
 |
| 図2 プレート運動再現装置 | 図3 寒天を用いた断層形成実験 |
地震が起こす現象の科学
午後は、地震によっておこる様々な現象の中で、特に(1)津波と(2)液状化現象について実験を通して理解することを目的とした。2つの実験班に分け、両テーマを交互に体験させる。
1.津波
津波が大きな被害をもたらす理由を模擬する実験を行う。津波発生装置は、アクリル板で製作した水槽に水を入れ水槽の端でアクリル板を押して波を発生させる装置である(図4)。津波がリアス式海岸に押し寄せた時に被害が大きくなるという事例から、a.水域幅の変化、b.水深の変化に着目させる。aは、木片を用いて幅が徐々に狭くなる水槽で津波を発生させ、各地点における波の高さを記録する。bは、水深を3段階に変化させ、距離1mの波の伝播時刻を測定する。生徒は、波の発生係・測定係・記録係の役割を担う。
この実験で幅が狭くなると波が高くなり、水深が浅いと速度が速くなる、さらに、水深が深いと、波の発生に大きな力が必要で、巨大な力で津波が発生することを確認する。上記2つの効果が現れるリアス式地形の湾岸を模擬した発泡スチロール製模型を水槽にはめ込み津波を発生させる。一般的な短波長の連続的な海の波と津波の岸への遡上の様子を観察し津波は陸上に被害を疑似体験させる。
 |
 |
| 図4 津波の発生実験の様子 | 図5 液状化を観察する様子 |
2.液状化現象
液状化現象が起きる条件を理解することを目的とする。 まず、液状化現象の被害写真から、実際の状態を理解する。軟弱な地盤な上に建物がある状態を、水を含んだ砂の上に建物の模型をおいた水槽で模擬し、容器下より振動を与え砂が流動的に動く現象―液状化現象を観察させる(図5)。さらに、振動時の砂の状態を手で触って体感する。水量や振動強度を変化させた実験を行うことにより、液状化が起きる条件として、砂、水、強振動、が必要であることを理解させる。これらの実験を通して、地盤強度の弱い海岸沿いの埋め立て地付近で、強い地震の揺れがあると液状化現象が起きやすいことを理解する。
結果とまとめ
学生らは、中学生が学んだ内容を今後の生活に役立ててほしいという思いも込めて地震をテーマとしたが、授業を通して,中学生たちは学生の想像以上に事前から地震に対する興味や知識を持っており、授業の進行は生徒らに助けられたと言う感もある。今回地震をテーマとして取りあげ,学生達が手作りで実験を工夫し、授業を作り上げたことに関しては、十分評価できる。学生が実施したアンケートでは、ほとんどが学生の指導、理解度という点では好意的な評価をされていた。
自然現象の中でも野外観察から始まる地学という科目は,初等教育の中では、野外観測が困難なため、ほとんど教科書などの本や模擬実験で終わってしまう。このような実験教室のような機会に、是非野外観察を取り入れることを期待したが、学生自身がこのような教育体系の中で育成されてきた経緯からか、地学の授業は、「本来外へ出向いて体験・観察すべき事柄や自分たちの目で確認することのできないくらい地中で起きる出来事を,実験室という小さい範囲の中で表現しなければならない」と考え、室内の模擬実験に終始する傾向があったように見受けられる。
学生は、当初テーマの設定に時間を費やした。「地学」という枠組みの中で、「スケールの大きさ」をコンセプトにしたいという思いから、当初「太陽系の大きさをグランドで示す」実験を考えたが、その後の具体的な教育内容に進展せず、テーマを変更した経緯もある。教育実習なども未経験の学生が、実質3ヶ月の中で1日の実験授業を作り上げるために必要とする時間は「授業」の枠では到底収まりきらないことであることは、教員側でも今後考慮していく必要があると考えられる。
 Shaky Earth Project~The science of phenomena due to earthquakes(2004)
Shaky Earth Project~The science of phenomena due to earthquakes(2004)
Introduction
Introduction
In Friendship Outreach Meeting, third year students specializing in science education develop science experimental programme as a part of their courses and give junior high students guidance in them at Miyagi University of Education during summer holidays.
Goal
It is the goal of this programme to understand the mechanism of earthquakes, phenomena caused by earthquakes especially mechanisms of Tsunami and liquefaction through the experiments. Following the big earthquake in 2003 off Miyagi coast or and another big earthquake highly likely, is one of the immediate disasters for the junior high students in Miyagi. Consequently, the students determined to teach the mechanism of earthquakes and other phenomena to understand more about earthquakes through the experiments.
Programme
In the morning the mechanism of earthquakes were taught with experiments and observations and in the afternoon the phenomena associated with earthquakes were.
Teaching Plan
| Goal | What to do |
To understand mechanism of earthquakes
Correlation between hypocentre distributions and locations of plate boundaries. Fault activity causes earthquakes. |
|
To understand phenomena associated with earthquakes
The narrower a range of land features is, the higher a wave height is. Much water may cause liquefaction. |
|
Mechanism of earthquake
Mechanism of earthquakes
Discussing a familiar earthquake experience related to the generation mechanism of the earthquake for the introduction, and the hypocentre and the epicentre of a structural movement and the earthquake,and other earthquake terms related to the movement in the plate were studied in the morning.
- Introduction:Motivating from their experiences of the earthquake, the definition of earthquake terms is confirmed, and from the observation of the epicentre distribution in the world, the bias of the hypocentre distribution are demonstrated.
- The hypocentre distribution and the movement in the plate of the region around Japan: The fact that the hypocentre distribution in the region around Japan correlates to the position of the plate is observed from the observation of the hypocentre distribution according to depth (Figure 1). In addition, the plate is dragged with the reproduction of the movement in the plate device (Figure 2) and movement of plates is observed and modeled.
- The earthquake by the fault movement: A shallow fault type earthquake such as inland active faults, besides the plate boundary type earthquake, is made to be read from the hypocentre distribution. The model experiment of the fault formation (Figure 3) that observes the cracking by putting the hexahedron agar likened to the earth hardened in the milk carton into an acrylic board without the upper surface and one side and pushing the agar from side is executed, and the photograph of the fault of the Tohoku Institute of Technology Aoba-yama ground is observed.
 |
 |
| Figure 1: Left: Hypocentre distribution sheet. The one that Hypocentres of earthquakes that occur in the past ten years around Japan (Science Chronological Table) were plotted on acetate in every 10km from surface of the earth to depth of 100km. Right: A pupil is observing the feature of seismic centre distribution piling up and down the hypocentre distribution sheet in order of depth. | |
 |
 |
| Figure2: Plate motion simulator | Figure3: Fault formation experiment by agar |
The science of phenomena due to earthquakes
In the afternoon, it aimed to understand (1) Tsunami and (2) liquefaction especially in phenomenon due to earthquakes through the experiments. Pupils are divided into two groups, and both themes are experienced alternately.
- Tsunami
- Liquefaction
The experiment that simulates the reason Tsunami causes big damage is conducted. The Tsunami tidal wave generation device (Figure 4) is a device that generates the wave by filling the water tank made of acrylic board with water and pushing an acrylic board on the edge of the tank. When the tidal wave surged in the ria type seashore, when damage becomes large, from this case, pupils are told to pay attention to a. the change of the width of water and b. the change of the depth of water. In a, the tidal wave is generated by using the chip in the water tank that width narrows gradually, and the height of the wave at various locations is recorded. In b, depth is changed to three stages, and the spread time of the wave of the distance 1m is measured. The pupils play the role of the person in charge of generation, the person in charge of the measurement, and the person in charge of the record.
It is confirmed that wave rises when width of geographical features narrows, speed quickens when depth is shallow, and big power is necessary for generating wave when depth is deep, so Tsunami is generated by huge power. The model made of the styrene foam that imitates the bay shore in the ria shoreline type geographical features where two above-mentioned effects become visible is set into the water tank and waves are generated. General sea wave that is continuous and short wavelength and how the wave rises ashore are observed and simulated damages by Tsunami.
 |
 |
| Figure 4: Appearance of experiment of generation Tsunami | Figure5: Observing Liquefaction |
It aims to understand the conditions under which liquefaction occurs. First of all, the actuality is understood from the damage photograph of liquefaction. Imitating a building on the weak ground by putting a model of a building onto the sand that contains water in a water tank and simulating the moving phenomenon (liquefaction) by generating vibration under the container(Figure 5). In addition, the state of the sand when vibrating is experienced touching by the hand.It makes clear that water, and strong vibration are necessary as the condition that liquidizing occurs from conducting the experiment that changes the volume of water and vibration strength. It is understood through these experiments that liquefaction occurs easily when there is the shake of a strong earthquake in the vicinity of the reclaimed ground along the coast to which ground strength is weak.
Results and Discussion
The junior high school students had more interest and previous knowledge about earthquakes than they imagined. They helped the progress of the class. It is appreciable enough this time for the students' taking up the earthquake as a theme, devising the experiment handmade, and having made up the class. In the questionnaire that the student executed, most were favourably evaluated in the point of understanding and guidance level.
The subject of physical geography that starts from the outdoors observation mostly ends learning only by textbooks or experiments in classrooms in the elementary education because of the difficulty of the field observation. At the chance like this time, though the outdoors observation was expected to be taken by all means, the students seemed to think as, "It is necessary to express the event that occurs in too deep place to see by eyes or things that should be observed in the outdoor in a laboratory." , that meant they tended to focus.
The students took time to decide the theme. In the frame "Physical geography", "The size of the solar system is shown in the playground" experiment was shown from the concept of "Size of the scale" at first, however the theme had to be changed because it didn't progress to a concrete educational content afterwards. It is to be considered in the future also on the teacher side that three months is not enough time for the students who have not done practice teachings to finish making up the experiment class for a whole day.